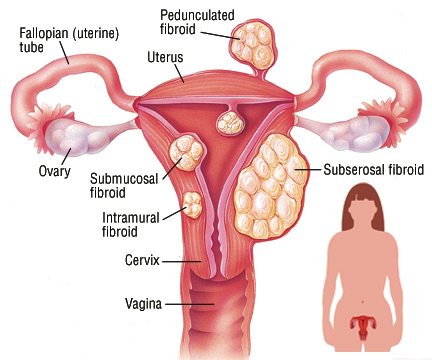
Minimally Invasive ways of treating Fibroids
There isn’t one way of treating fibroids. The options can vary from simple ones like supportive treatment to radical treatment such as hysterectomy. There are many important factors to consider such as age, size and location of fibroids, fertility aspirations and more importantly your symptoms and your wishes.
Once symptomatic, most fibroids need to be surgically removed. Removal of fibroid is recommended in women with symptoms of Abnormal Uterine bleeding, Pain during menstruation, Pressure symptoms or Infertility.
There different minimally invasive ways of removing fibroids, it can either be done laparoscopically or through hysteroscopy.
Laparoscopic Myomectomy
Laparoscopic Myomectomy is a procedure in which fibroids are removed from the uterus through small incisions in the abdomen while retaining the uterus. Even large and multiple fibroids can be removed with laparoscopic myomectomy. This has the advantages of faster recovery from surgery, very little post-operative pain, next-to-no scarring on the abdomen. This is the best treatment option for women with fibroids who wish to have children in the future.
Laparoscopic fibroid removal surgery is usually performed as day care surgery under general anesthesia. The advantage of a laparoscopic myomectomy over an open abdominal myomectomy is that, in a laparoscopic procedure, 3-4 very small incisions are used rather than one larger incision. The procedure can take one to three hours, depending on the number, size, and depth of the fibroids within the uterine muscle wall.
Following laparoscopic myomectomy most women are able to leave the hospital within 24 to 36 hours. Because the incisions are small, recovery is associated with minimal discomfort. Patients are able to sit up and walk around 6 hours after the surgery. Women usually resume to normal work and travel within 7-10 days.
How is a Laparoscopic Myomectomy done?
During this procedure a laparoscope (a thin fiber-optic device that transmits light and a video image) is inserted through a small incision, usually in the navel, to view the uterus. The image from the camera attached to the end of the laparoscope is seen on a video monitor. Three small (5mm) incisions are made in the lower abdomen and instruments are inserted through these incisions to perform the surgery. The fibroids are enucleated from the uterus and removed. Following removal of the uterine fibroids, the openings in the uterus are stitched to ensure proper healing.
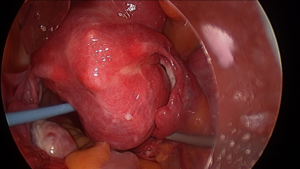
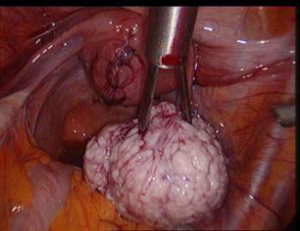
Is Laparoscopic Morcellation a safe procedure for fibroid specimen removal?
Morcellation involves cutting uterine or fibroid tissue into smaller pieces to allow removal laparoscopically, vaginally or through smaller cuts on your abdomen. This is often done using a device called a morcellator which electrically or mechanically cuts the tissue into smaller pieces.
One of the risks mentioned with morcellation is Small pieces of benign (non-cancerous) fibroid tissue could be left inside abdomen, if the surgeon is not well experienced enough. These small fibroid pieces may then attach to the internal organs in abdomen where they can continue to grow slowly. The risk of this happening is thought to be 1 in 120 (uncommon) to 1 in 1200 (rare). Rarely Morcellation of fibroid that could contain an unexpected cancer called uterine sarcoma. Morcellation of these type of fibroid without a bag increases the risk of spread of the cancerous tissue.
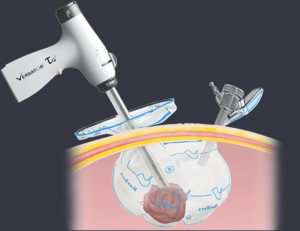
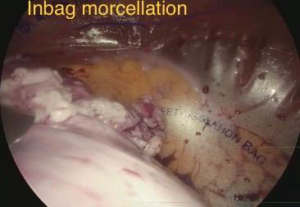
Benefits of Inbag Morcellation:
Now a day’s majority of experienced laparoscopic surgeons perform inbag morcellation to prevent the spread of myoma tissues. while doing inbag morcellation the fibroid is placed inside a bag and morcellated so that there will be absolutely no risk of spread of tissue with all the benefits of laparoscopy .Laparoscopic Morcellation allows the removal of a large fibroid or uterus through small cuts on your abdomen (keyhole surgery) or through your vagina. This means, less pain after surgery, reduced risk of infection, reduced risk of blood clots in the legs or lungs, a shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery. Women who is undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy should discuss with her doctor about the mode of specimen removal and ask for inbag morcellation.
Who should perform Laparoscopic Myomectomy?
The procedure is very safe and effective when performed by a properly trained physician. Not all surgeons are trained in laparoscopic surgery; because of the small size of the incisions, and the special instruments which are used. Removing uterine fibroids laparoscopically requires special training and expertise. An expert laparoscopic fibroid surgeon can remove numerous fibroids in a single operation, and also fibroids of very large size.
Many gynecologists have not been trained to suture with laparoscopic instruments, and some may even say that laparoscopic surgery is not possible. It is often a good idea to get a second opinion from an expert gynecologist who performs laparoscopic myomectomies on a regular basis to see if this procedure is feasible for you.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy
Hysteroscopic fibroid removal is a technique that can be performed for fibroids which are within or bulging into the uterine cavity (submucosal fibroid). Only women with submucosal fibroids are eligible for this type of myomectomy. Fibroids located within the uterine wall cannot be removed with this technique. Hysteroscopic myomectomy is an out-patient surgical procedure. Patients go home after 4-5 hours of observation in the recovery room. Recovery time is generally only few days. There are no scars on the skin after the procedure.
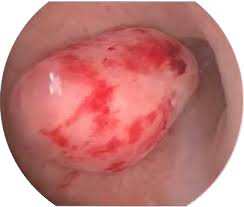
Hysteroscopic View Submucous Fibroid
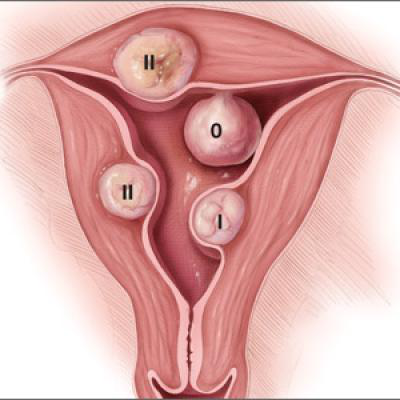
Hysteroscopic View Submucous Fibroid
Hysteroscopic removal of fibroids involves inserting a small fiber-optic device called a hysteroscope through the cervix to view the uterus from the inside. Hysteroscopes are so thin that they can fit through the cervix with minimal or no dilation. Because the instruments are inserted through the cervix, no abdominal incisions are needed. A hysteroscope that uses high-frequency electrical current to cut or coagulate tissue, is then inserted to remove the fibroids or a hysteroscopic morcellator can be used instead of resectoscope to avoid the usage electrical current. The fibroid can then be removed through the cervix.
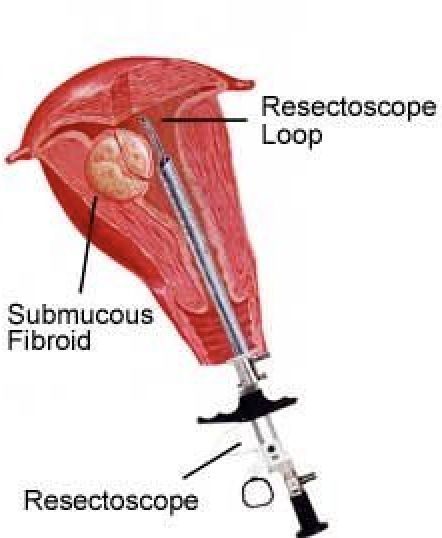
This procedure is done as an “outpatient” basis under general anesthesia. It takes about 30 – 60 minutes to complete the procedure depending on the size & number of submucous fibroid and the expertise of the surgeon
